
What is quartz?
Quartz is a mineral of crystal structure consisting of silica. Quartz occurs almost everywhere in the earth's crust and is included in rocks such as sandstone, quartzite, flint, granite, slate and gneiss.
The small particles of quartz dust can get into the alveoli, where the body cannot get rid of the particles. The particles are then instead encapsulated in the alveoli so that the volume of the lungs gradually decreases. This condition is called stone dust lung or silicosis. When the disease has spread, it is noticeable by becoming more easily out of breath, after a while even at rest. This also increases the load on the heart.
Another common disease, which mainly affects smokers but which can also affect those who have been in quartz dust a lot, is COPD. Quartz dust also significantly increases the risk of developing lung cancer.
Silicosis have a long latency of 10-30 years. That is why it is so important to protect oneself already today when working in exposed and harmful environments where quartz stone and construction dust can occur.
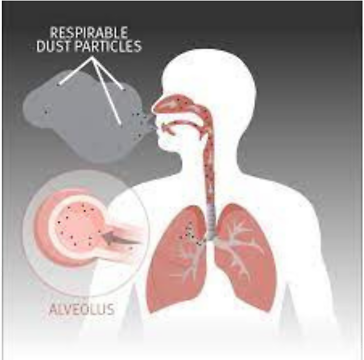
In addition to the obvious work environments where quartz dust can occur (sand, gravel, stone, concrete and rock handling), quartz dust can be present during construction and civil engineering work.
Other areas that the Swedish Work Environment Authority mentions are steel and metal production, porcelain and ceramics manufacturing, glass and abrasive products manufacturing.
Also production of glass wool, paint, plastic and glue production as well as operations at foundries, asphalt plants, root canal handling indoors and dental laboratories as well as sand collection from streets, among other places.

If a respiratory protection is used to protect against dust, particles, bacteria and aerosols, it needs to be fitted with a particle filter.
Particulate filters are marked with P and are available in three protection classes:
P3 - Is the most efficient filter. Distinguishes Separates more than 99.95% of dust, bacteria, particles and aerosols.
P2 - Is second most effective. Distinguishes Separates 94% of dust, bacteria, particles and aerosols.
P1 - Is least effective. Separates 80% of dust, bacteria, particles and aerosols.